
Image courtesy of renjith krishnan at FreeDigitalPhotos.net

The Renal System
The renal system (also known as the urinary system has many functions including:
-
Excretion of metabolic waste products produced by the cells
-
Removal of hormones, drugs, and other foreign materials
-
Regulation of water, electrolytes e.g. potassium, sodium etc and PH balance
-
Regulates blood volume by controlling the amount of water removed from the blood
-
Secretion of erythropoietin, a hormone that stimulates red blood cell formation in the bone marrow
-
Vitamin D synthesis
-
Regulates blood pressure
Organs of the renal system
-
Kidneys
-
Bladder
-
Urethra
-
Ureters
Kidneys
-
Located near the middle of the back, one on either side of the spine
-
Bean-shaped, about the size of a fist. Consist of an outer cortex and inner medulla
-
Have a very rich blood supply, to allow blood to pass through in large amounts so that it can be filtered to remove all the waste products
-
The main blood supply carrying blood to each kidney is called the renal artery
-
The renal veins carry the cleaned blood away from each kidney
Bladder
-
Hollow muscular organ located in the pelvic region
-
Its size and shape varies on how much urine is stored in it
-
Have two openings at the top where the ureters, which extend from the kidneys, drain urine into the bladder
-
There is one opening at the bottom where the urethra allows the urine to pass from the bladder out of the body
-
The female urethra lies in front of the anus and the vagina and is about 3.8cm long
-
The male urethra runs through the penis and is about 20cm long

Image by Sunshineconnelly at English Wikibooks - Transferred from en.wikibooks to Commons by Adrignola using CommonsHelper., CC BY 3.0,
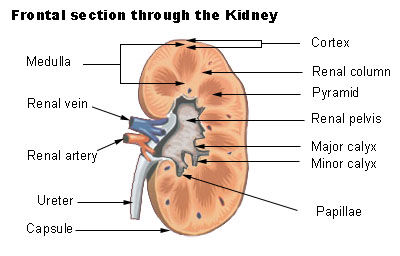

Image by OpenStax College - Anatomy & Physiology, Connexions Web site. http://cnx.org/content/col11496/1.6/, Jun 19, 2013., CC BY 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=30148530